Estimate USDJPY after 1 day based on 10 years of data by using scikit-learn
# import libraries import pandas as pd import numpy as np import talib as ta from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, precision_score, recall_score, confusion_matrix import optuna import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import seaborn as sns
# Check the shape print(df0.shape)
# Check the data summary = df0.describe() print(summary)
# # Display information about the DataFrame df0.info()
df0["Date"] = pd.to_datetime(df0["Date"])
# Get the oldest and latest dates
oldest_date = df0["Date"].min()
latest_date = df0["Date"].max()
print("Oldest Date:", oldest_date)
print("Latest Date:", latest_date)df0["Date"] = pd.to_datetime(df0["Date"])
# Get the oldest and latest dates
oldest_date = df0["Date"].min()
latest_date = df0["Date"].max()
print("Oldest Date:", oldest_date)
print("Latest Date:", latest_date)Oldest Date: 2003-09-15 00:00:00
Latest Date: 2022-11-11 00:00:00
# Load and clean the data for df1
df1 = pd.read_csv("")
df1["Date"] = pd.to_datetime(df1["Date"], format="%m/%d/%Y") # Specify the correct date format
# Concatenate DataFrames
df = pd.concat([df0, df1])
# Calculate oldest and latest dates
oldest_date = df["Date"].min()
latest_date = df["Date"].max()
print("Oldest Date:", oldest_date)
print("Latest Date:", latest_date)Oldest Date: 2003-09-15 00:00:00
Latest Date: 2022-11-11 00:00:00
print(df.shape)
(5218, 7)
df.info()
<class ‘pandas.core.frame.DataFrame’>
Index: 5218 entries, 0 to 217
Data columns (total 7 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype — —— ————– —–
0 Date 5218 non-null datetime64[ns]
1 Price 5218 non-null float64
2 Open 5218 non-null float64
3 High 5218 non-null float64
4 Low 5218 non-null float64
5 Vol. 0 non-null float64
6 Change % 5218 non-null object
dtypes: datetime64[ns](1), float64(5), object(1) memory usage: 326.1+ KB
# Drop the "Vol." column from df
df = df.drop("Vol.", axis=1)
# Check the shape of df after dropping the column
print("Shape of df after dropping 'Vol.' column:", df.shape)Shape of df after dropping ‘Vol.’ column: (5218, 6)
# Identify columns with all null values
null_columns = df.columns[df.isnull().all()]
# Drop columns with all null values
df = df.drop(columns=null_columns)
# Check the shape of df after dropping null columns
print("Shape of df after dropping null columns:", df.shape)Shape of df after dropping null columns: (5218, 6)
# print the unique column names in df
print("Unique column names in df:", df.columns.tolist())Unique column names in df: [‘Date’, ‘Price’, ‘Open’, ‘High’, ‘Low’, ‘Change %’]
#All subsequent calculations use the closing rate close = np.array(df["Price"]) #Create an empty dataframe to contain features df_feature = pd.DataFrame(index=range(len(df)),columns=["SMA5/current", "SMA20/current","RSI","MACD","BBANDS+2σ","BBANDS-2σ"]) #Ccalculate technical indicators (features used in this training) using talib and put in df_feature #Simple moving average uses the ratio of the simple moving average to the closing price of the day as the feature value df_feature["SMA5/current"]= ta.SMA(close, timeperiod=5) / close df_feature["SMA20/current"]= ta.SMA(close, timeperiod=20) / close #RSI df_feature["RSI"] = ta.RSI(close, timeperiod=14) #MACD df_feature["MACD"], _ , _= ta.MACD(close, fastperiod=12, slowperiod=26, signalperiod=9) #Bollinger bands upper, middle, lower = ta.BBANDS(close, timeperiod=20, nbdevup=3, nbdevdn=3) df_feature["BBANDS+2σ"] = upper / close df_feature["BBANDS-2σ"] = lower / close
df["the day before_float"] = df["Change %"].apply(lambda x: float(x.replace("%", "")))
#How to categorize the % of previous day. Divide as much as possible so that the sample of each class is equal
def classify(x):
if x <= -0.2:
return 'down'
elif -0.2 < x < 0.2:
return 'even'
elif 0.2 <= x:
return 'up'
df["the day before_classified"] = df["the day before_float"].apply(lambda x: classify(x))
#Shift the data you want to teach by one day (you know what I mean)
df_y = df["the day before_classified"].shift()# Reset the index of df0_y to ensure uniqueness df_y = df_y.reset_index(drop=True) # Concatenate df0_feature and df0_y with reset index df_xy = pd.concat([df_feature, df_y], axis=1) df_xy = df_xy.dropna(how="any")
# print("Shape of df_xy:", df_xy.shape)
print("Number of samples in df_xy:", len(df_xy))
X_train, X_test, Y_train, Y_test = train_test_split(
df_xy[["SMA5/current", "SMA20/current", "RSI", "MACD", "BBANDS+2σ", "BBANDS-2σ"]],
df_xy["the day before_classified"],
train_size=0.8,
random_state=42
)
print("Shape of X_train:", X_train.shape)
print("Shape of X_test:", X_test.shape)
print("Shape of Y_train:", Y_train.shape)
print("Shape of Y_test:", Y_test.shape)Shape of df_xy: (5185, 7)
Number of samples in df_xy: 5185 Shape of X_train: (4148, 6)
Shape of X_test: (1037, 6)
Shape of Y_train: (4148,)
Shape of Y_test: (1037,)
X_train, X_test, Y_train, Y_test = train_test_split(df_xy[["SMA5/current", "SMA20/current","RSI","MACD","BBANDS+2σ","BBANDS-2σ"]],df_xy["前日比_classified"], train_size=0.8)
def objective(trial):
min_samples_split = trial.suggest_int("min_samples_split", 2,16)
max_leaf_nodes = int(trial.suggest_discrete_uniform("max_leaf_nodes", 4,64,4))
criterion = trial.suggest_categorical("criterion", ["gini", "entropy"])
n_estimators = int(trial.suggest_discrete_uniform("n_estimators", 50,500,50))
max_depth = trial.suggest_int("max_depth", 3,10)
clf = RandomForestClassifier(random_state=1, n_estimators = n_estimators, max_leaf_nodes = max_leaf_nodes, max_depth=max_depth, max_features=None,criterion=criterion,min_samples_split=min_samples_split)
clf.fit(X_train, Y_train)
return 1 - accuracy_score(Y_test, clf.predict(X_test))
study = optuna.create_study()
study.optimize(objective, n_trials=100)
print(1-study.best_value)
print(study.best_params)# Create and train a RandomForestClassifier
model = RandomForestClassifier()
model.fit(X_train, Y_train)
# Predict the target values for the test data
Y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
# Calculate the accuracy, precision, recall
accuracy = accuracy_score(Y_test, Y_pred)
precision = precision_score(Y_test, Y_pred, average='weighted') # You can also use 'macro' or 'micro'
recall = recall_score(Y_test, Y_pred, average='weighted') # You can also use 'macro' or 'micro'
print("Accuracy:", accuracy)
print("Precision:", precision)
print("Recall:", recall)Accuracy: 0.5660559305689489
Precision: 0.5637978876125685
Recall: 0.5660559305689489
# Create and train a RandomForestClassifier
model = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100, random_state=1)
model.fit(X_train, Y_train)
# Get feature importances
feature_importances = model.feature_importances_
# Create a DataFrame to associate features with their importances
importance_df = pd.DataFrame({"Feature": X_train.columns, "Importance": feature_importances})
importance_df = importance_df.sort_values(by="Importance", ascending=False)
# Print or visualize the feature importances
print(importance_df)
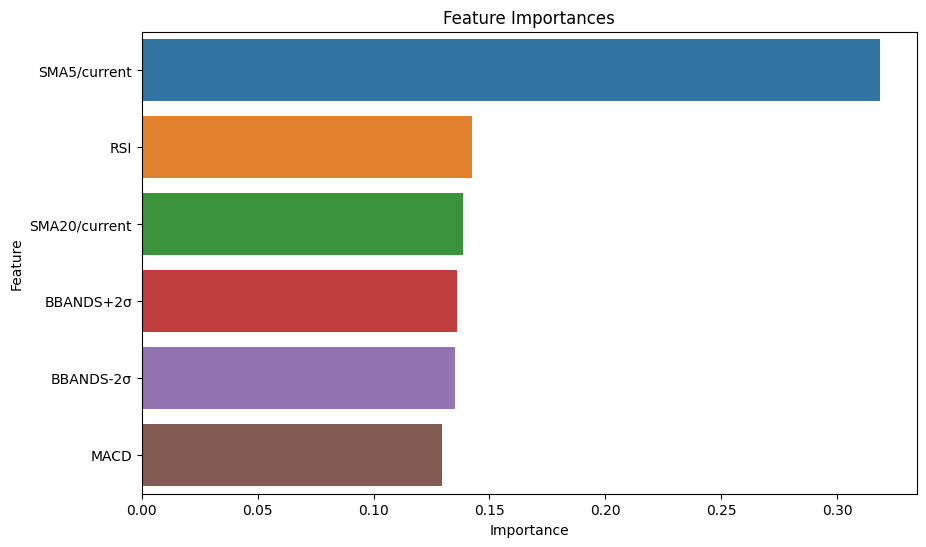
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
sns.barplot(x="Importance", y="Feature", data=importance_df)
plt.title("Feature Importances")
plt.xlabel("Importance")
plt.ylabel("Feature")
plt.show() Feature Importance
0 SMA5/current 0.318452
2 RSI 0.142284
1 SMA20/current 0.138512
4 BBANDS+2σ 0.135807
5 BBANDS-2σ 0.135339
3 MACD 0.129607